Early History
The Fortezza is built on a hill called Paleokastro (meaning “Old Castle”), which was the site of ancient Rhithymna’s acropolis.
Between the 10th and 13th centuries, the Byzantines established a fortified settlement to the east of the hill. It was called Castrum Rethemi, and it had square towers and two gates.
The fortifications were repaired by Enrico Pescatore in the beginning of the 13th century. After Crete fell to the Republic of Venice, the settlement became known as the Castel Vecchio or Antico Castello, which both mean “old castle”.
Under Venetian rule, a small harbour was built in Rethymno, which became the third most important city on Crete after Heraklion and Chania.
On 8 April 1540, a line of fortifications began to be built around the city. The walls were designed by the architect Michele Sanmicheli, and were completed in around 1570.
These fortifications were not strong enough to withstand a large assault, and when Uluç Ali Reis attacked in 1571, the Ottomans captured and sacked the city.
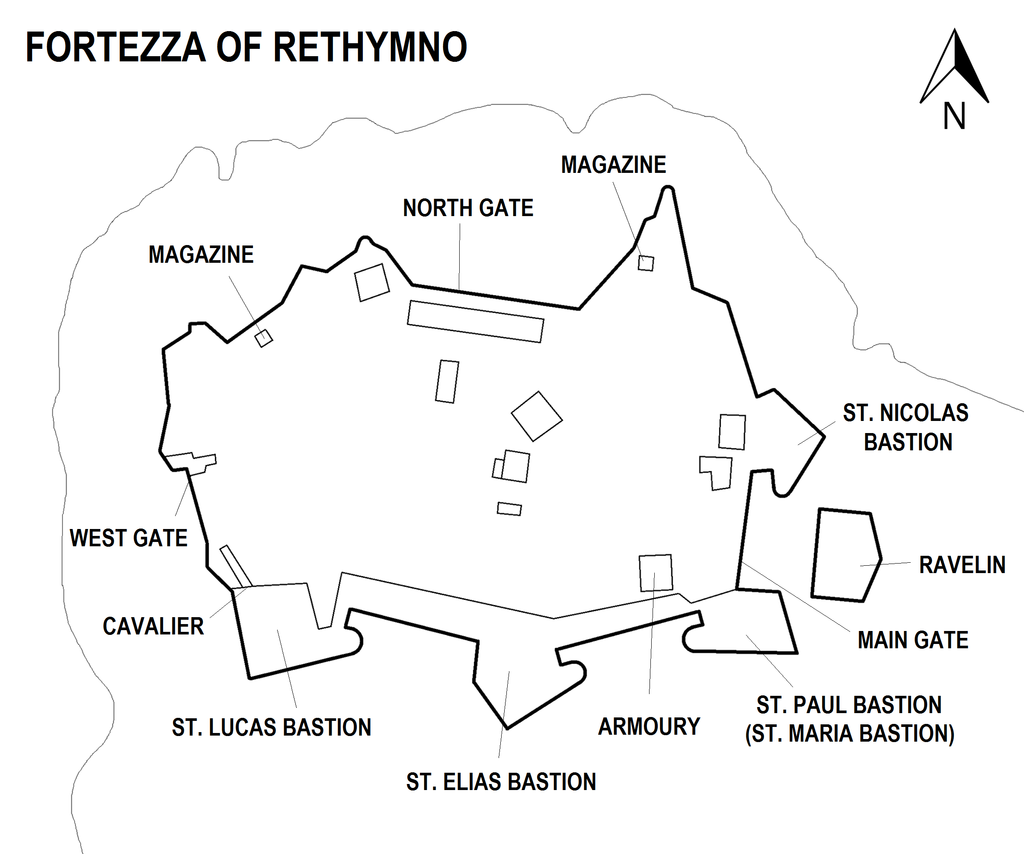




Construction and latest Venetian rule
Following the fall of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571, Crete became the largest remaining Venetian overseas possession.
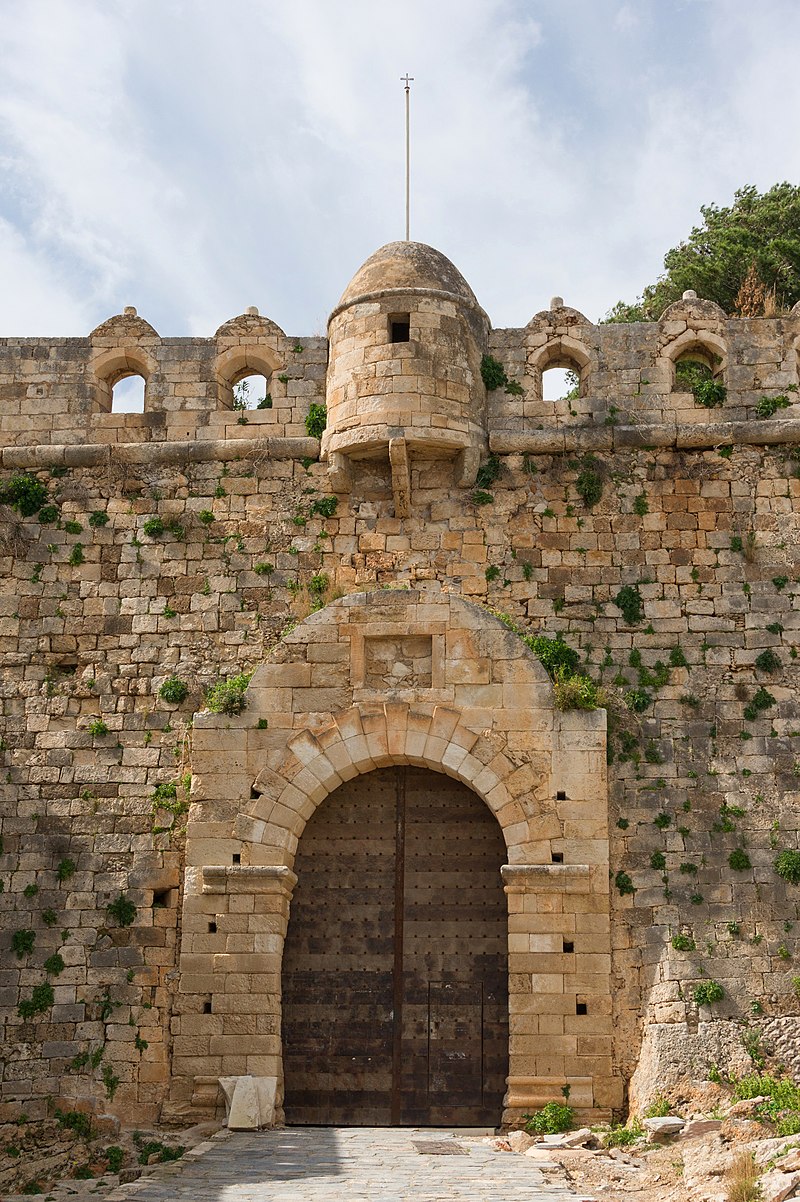
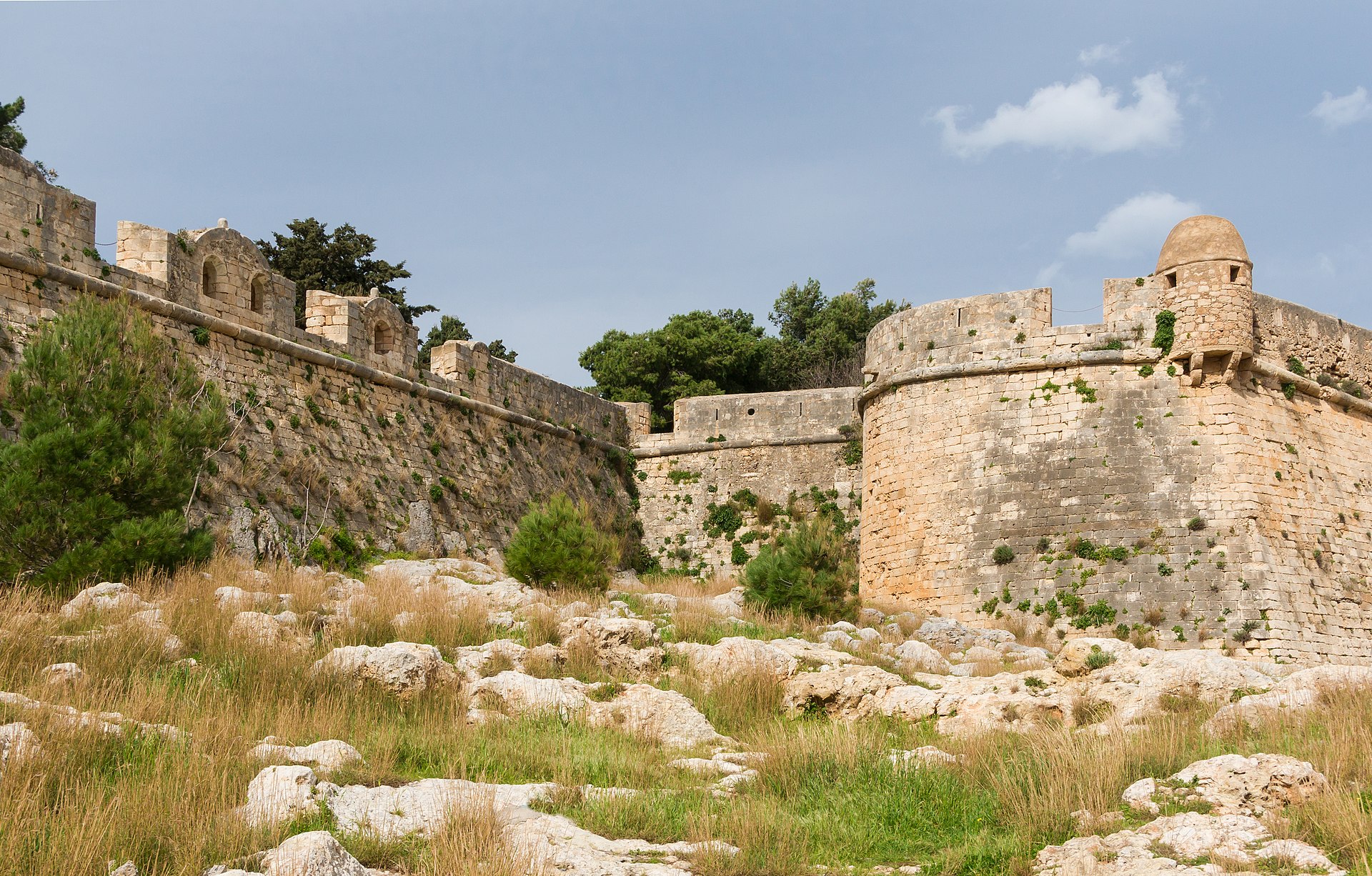
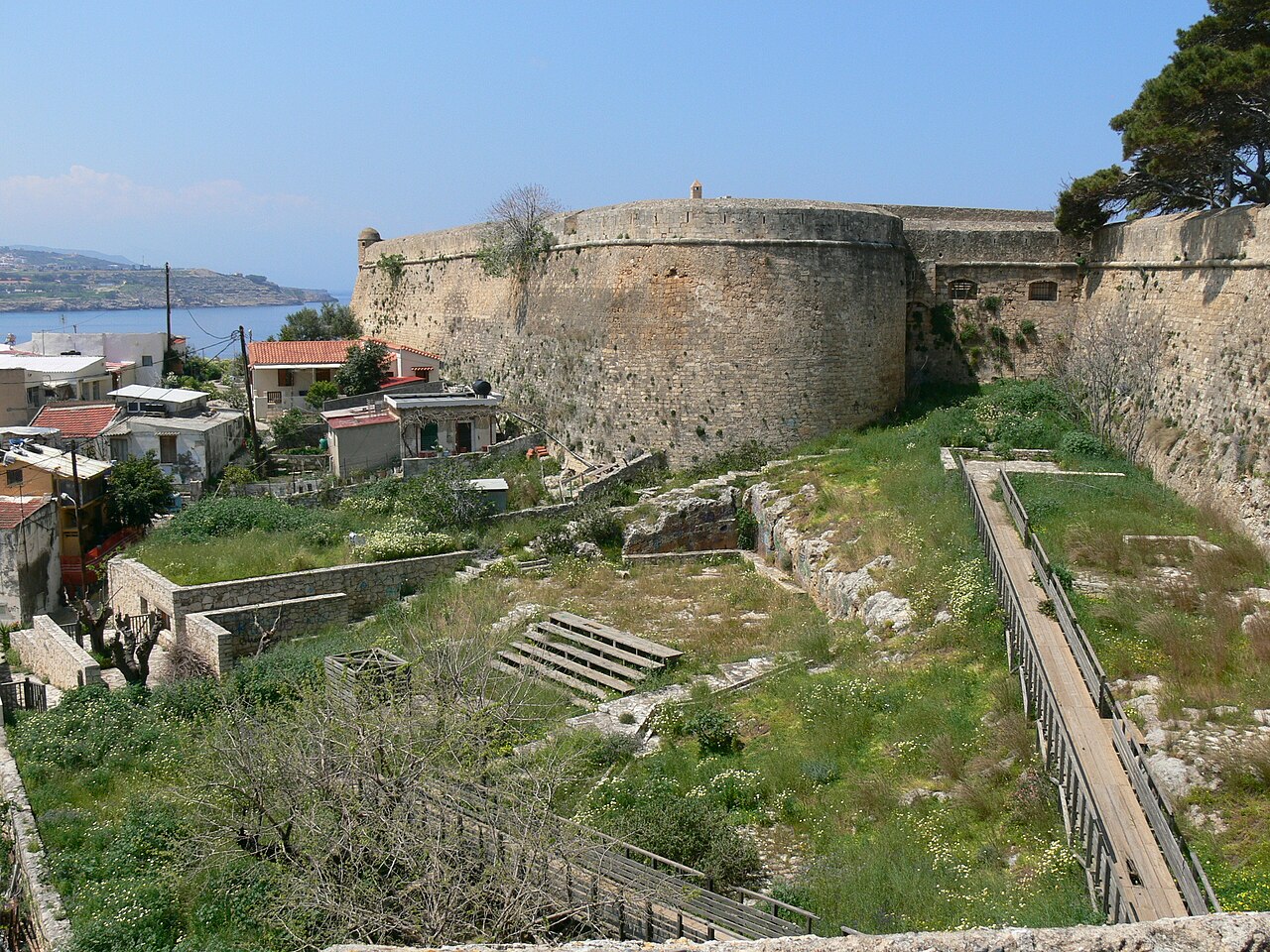
Since Rethymno had been sacked, it was decided that new fortifications needed to be built to protect the city and its harbour. The new fortress, which was built on the Paleokastro hill, was designed by the military engineer Sforza Pallavicini according to the Italian bastioned system.
Construction began on 13 September 1573, and it was complete by 1580. The fortress was built under the master builder Giannis Skordilis, and a total of 107,142 Cretans and 40,205 animals took part in its construction.
Although the original plan had been to demolish the old fortifications of Rethymno and move the inhabitants into the Fortezza, it was too small to house the entire city. The walls along the landward approach to the city were left intact, and the Fortezza became a citadel housing the Venetian administration of the city. It was only to be used by the inhabitants of the city in the case of an Ottoman invasion.
Over the years, a number of modifications were made to the fortress. Nonetheless, it was never truly secure as it lacked a ditch and outworks, and the ramparts were rather low.
